Imagine waking up to a nightmare. Your website is hacked. Customer data is stolen, pages defaced, and your hard work is gone. Scary right?
Hackers never rest. They hunt for weak passwords, outdated plugins, and security gaps. One small flaw is all they need. But you can stop them.
Want to know how to secure your website from hackers? This guide will show you easy yet powerful ways to keep hackers out.
How to Secure Your Website from Hackers: 10 Proven Way

1. Use Strong Passwords and Multi-Factor Authentication
Weak passwords make hacking easy. Many still use “password,” “123456,” or their name. Hackers use brute-force attacks to guess passwords and get in.
Create strong passwords with Uppercase letters, Numbers, and Symbols. A good example: Xj@92!pQe&. Too hard to remember?
Use a password manager like 1Password, LastPass, or Bitwarden.

For extra protection, enable multi-factor authentication. Even if hackers get your password, they can’t get in without the second step. A code will be sent to your phone. Google Authenticator and Authy are great MFA apps.
2. Keep Software, Plugins, and Themes Updated
Outdated software is a hacker’s favourite target. If you don’t update your CMS, plugins, or themes, hackers exploit security holes to inject malware or steal data.
Keep everything up to date. If you use WordPress, go to Dashboard → Updates and install updates regularly.
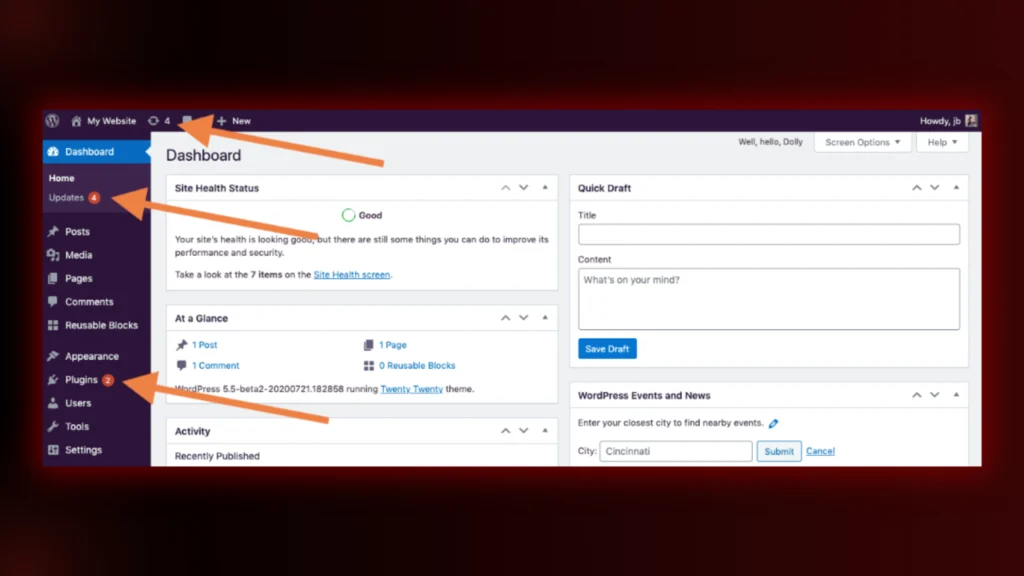
On Joomla and Magento, update plugins and extensions from the admin panel.
Delete unused plugins and themes. If you don’t use them, they can still be a security risk. Use WP-Optimize or Plugin Organizer to manage plugins and remove old ones.
3. Install an SSL Certificate and Use HTTPS
Hackers can intercept data between your site and visitors if there isn’t HTTPS. This means stolen:
- Passwords
- Payment details
- Personal information
An SSL certificate encrypts this data. Google also favours HTTPS sites in search rankings. Most hosting providers, like HostGator, Bluehost, and SiteGround, offer free SSL certificates.
Check your URL. If it starts with “http://” instead of “https://”, you need SSL.
4. Use a Web Application Firewall
A firewall blocks malicious traffic before it reaches your website. It acts as a filter, stopping:
- Hackers
- Bots
- Malware
Use the following Web Application Firewalls to protect your site:
These services detect threats in real-time and block suspicious IPs.
For eCommerce sites, Imperva WAF is great for stopping credit card fraud and data breaches. A good firewall is your first line of defence.
5. Install Security Plugins for Extra Protection
Security plugins scan for malware, limit login attempts, and block suspicious activities. Each CMS has dedicated security plugins:
- WordPress: iThemes Security, Wordfence
- Magento: Amnesty, Watchdog Pro
- Joomla: Jay HackGuard
These tools block brute-force attacks, malware injections, and unauthorized file changes. For extra security, SiteLock scans your website for threats.
6. Invest in Automatic Backups
If hackers attack, a backup can save you. Without one, you risk losing everything. Use automatic backup services like CodeGuard, UpdraftPlus (for WordPress), or Akeeba Backup (for Joomla). These tools save copies of your website daily.
Store backups offsite in the cloud or on an external server. Avoid keeping them on the same hosting server. It is because if hackers get in, they can delete everything.
7. Hide Your Login Page and Limit Login Attempts
Hackers use very strong attacks to guess your login password. They try thousands of combinations until they break in.
Change the default login URL to something unique. For WordPress, use WPS Hide Login to rename wp-admin to something like mysecurelogin123.
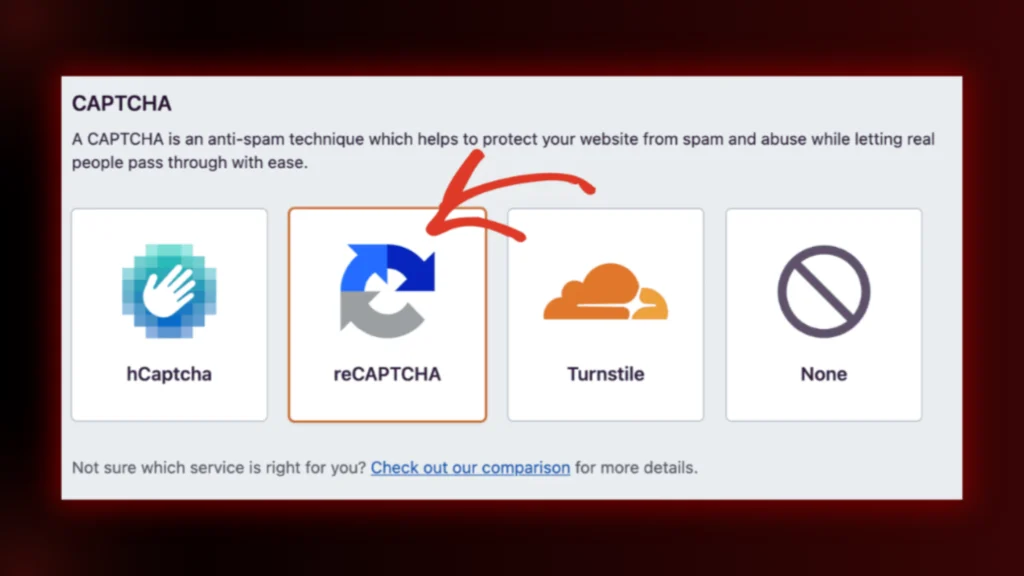
You can also limit login attempts to block repeated failed logins. Use Login LockDown, WP Limit Login Attempts, or Fail2Ban to block hackers after multiple failed tries. Add CAPTCHA verification for extra protection.
8. Protect Against SQL Injection & Cross-Site Scripting
Hackers use SQL injection or SQLi to steal databases. They insert malicious code into search bars or login forms. This lets them access user data, passwords and credit card details.
Use prepared statements and parameterized queries to stop SQL injections. For WordPress, you can install WPScan or Sucuri Security to scan for vulnerabilities.
Cross-site scripting is another threat. Hackers inject malicious JavaScript into your site and can steal cookies and session data. A Content Security Policy (CSP) stops this by blocking unauthorized scripts.
9. Monitor and Scan Your Site for Threats
Don’t wait for a hack. Scan your site regularly for malware and vulnerabilities.
Hackers don’t always make their attacks obvious.
You can use Sucuri, Wordfence or SiteLock to detect threats. Set up email alerts for unusual activity. Check Google Search Console for security warnings.
If your site is compromised, you can use the following tools to clean it up fast:
- MalCare
- Astra Security
- SiteGround Security
10. Restrict User Permissions & Secure File Uploads
Not everyone needs admin access. The more people with full control, the greater the risk.
Limit user roles to only what’s necessary. For example:
- Admins: Full control
- Editors: Can edit content but not install plugins
- Users: Can only comment or view
For file uploads, restrict file types to prevent hackers from uploading harmful scripts. Use MalCare or WP File Manager Security to scan uploaded files.
10 Symptoms of a Hacked Website

A hacked website can cause serious problems. It can lead to data theft and loss of customer trust. Recognizing the signs early can help you take action quickly. Here are the common symptoms of a hacked website:
1. Unexpected Website Changes
Your website may look different without your approval. The homepage might show strange content.
You may see pop-ups or get redirected to unknown sites. Hackers often add harmful scripts to damage your website’s reputation.
2. Website Becomes Slow or Unresponsive
Your website may load very slowly. It may crash frequently for no reason. Hackers can use your site for illegal activities. They may run scripts, send spam, or mine cryptocurrency. This uses up server resources and affects performance.
3. Unexplained User Account Activity
New admin accounts may appear in your CMS. Existing user passwords might change without permission. Hackers create new accounts to keep access even if you remove their malware.
4. SEO and Search Engine Warnings
Google may warn users that “This site may be hacked.” Your website may disappear from search results. It may rank for spam keywords. This happens when hackers inject harmful content.
5. Suspicious Traffic Spikes
Your website may get sudden traffic from unknown locations. Most of it may come from countries you don’t target.
Hackers use bots to scan for security holes. They may attempt brute-force attacks or inject malware.
6. Customers Report Security Issues
Visitors may report phishing emails from your domain. They might see strange pop-ups. Their browsers may show security warnings like “This site is not secure.”
7. Security Warnings from Hosting or Security Tools
Your hosting provider may suspend your website. Security tools may send alerts about malware.
You may get warnings about unauthorized file changes or unknown login attempts.
8. Unauthorized Changes in Files or Code
Hackers often modify core files. Important files like wp-config.php and .htaccess may change.
You may find unknown scripts in your hosting directory. Regularly checking your files can help detect this early.
9. Emails Not Being Delivered (Email Blacklisting)
Your emails may stop reaching customers. Users may report they didn’t receive emails from your website.
This happens when hackers use your site to send spam. Your domain may get blacklisted.
10. Sudden Drop in Website Performance
Your server may slow down. CPU and bandwidth usage may spike for no reason. Hackers might use your site for DDoS attacks or other malicious activities.
Also Read:
- How To Use APIs in Modern Web Development
- How To Create Interactive Websites For Better User Engagement
FAQs
1. What protects websites from hackers?
Protecting a website requires multiple security measures. These steps help keep hackers out and data safe.
- Strong passwords
- HTTPS encryption
- Firewalls
- Security plugins
- Regular updates
- Backups and malware scanners
2. How do I make sure my website is secure?
A secure website prevents data theft and cyberattacks. Follow these steps to strengthen protection.
- Use HTTPS
- Update software regularly
- Install security plugins
- Enable two-factor authentication
- Scan for malware
- Back up data frequently
3. Can I make my website secure for free?
Yes, securing a website doesn’t always require money. Many free tools offer strong protection.
- Free SSL certificates (Let’s Encrypt)
- Free security plugins (Wordfence, iThemes Security)
- Built-in hosting security features
4. How can online website operations be protected from hackers?
Keeping website operations secure ensures smooth functionality and user trust. These steps help safeguard online activities.
- Limit login attempts
- Use strong, unique passwords
- Enable firewalls and security plugins
- Keep all software and plugins updated
- Perform regular backups
- Use monitoring tools for threats
Need Help Securing Your Website?
Don’t let hackers ruin your hard work! If you need expert help to secure your website, Brand ClickX has you covered.
- Stronger security to keep hackers out
- Expert guidance on website protection
- Ongoing support for peace of mind
Let’s make your website safe and secure. Get in touch today!



