Let’s chat about something that often gets overlooked but is critical for SEO success: website page depth. If you’ve ever wondered why some pages on your website seem to get all the love from Google while others are practically invisible, page depth might be the culprit. And guess what? Internal linking is your secret weapon to optimize it.
Now, before diving in, let’s address the elephant in the room—what exactly is website page depth? Simply put, it’s how many clicks it takes to reach a specific page from your homepage. The deeper a page is buried, the harder it is for both users and search engines to find it. But don’t worry; by the time you finish reading, you’ll know how to make your site structure work for you. Ready? Let’s go!
Why Website Page Depth Matters
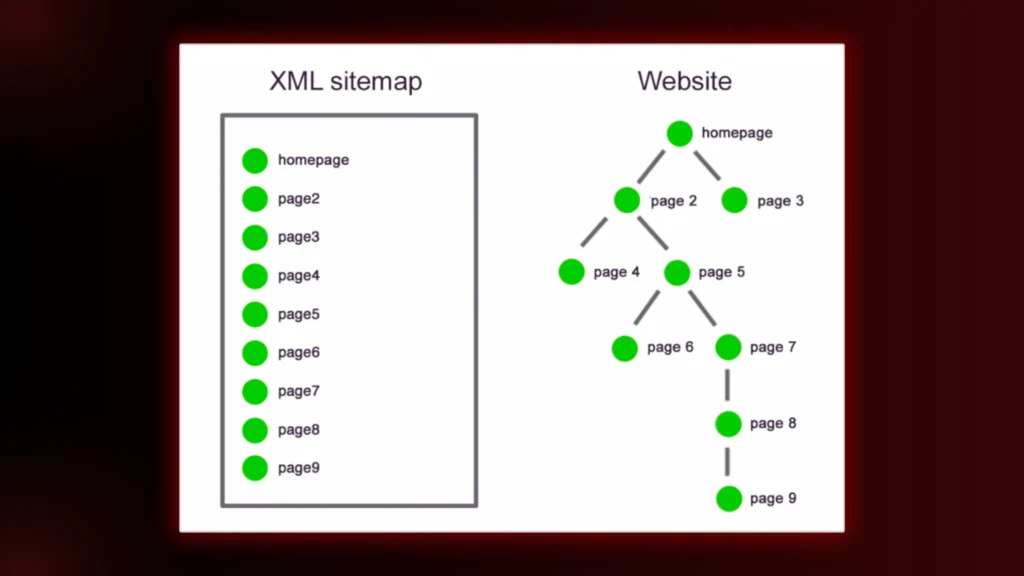
Imagine your website as a treasure map. Your content is the hidden treasures, and the start is the homepage, after the homepage, every internal link is a path. Your treasure buried too deep – say, five or six clicks deep — the chances are good that most people (and search engines) aren’t going to bother.
Here’s why this matters:
- User Experience (UX): Nobody likes clicking endlessly to find what they need. A shallow website structure keeps users happy and engaged.
- Search Engine Crawling: Search engines prioritize pages that are easy to find. If a page is buried too deep, it might not even get indexed.
- Link Equity Distribution: Shallow pages receive more link equity, which boosts their rankings.
So, what’s the ideal depth? Along with that, try to limit yourself to three clicks from the homepage to any page to improve readability. Sounds simple enough, right? However, a good internal linking strategy is needed to achieve this.
The Role of Internal Linking in Reducing Page Depth

As internal links are like bridges connecting to different segments within your website. They help both the users and search engines deal with your pages and equally distribute the link equity. This is how they aid with page depth:
1. Flattening Your Site Structure: By strategically linking deeper pages to high-level ones, you reduce the number of clicks needed to reach them.
2. Highlighting Important Content: Internal links signal to search engines which pages are most valuable.
3. Improving Crawlability: Links make it easier for search engine bots to discover and index all your pages.
For instance, you have a e-commerce shop with product pages buried deep down in subcategories, and blog posts and category pages on the other hand, internal links from the blog posts or category pages can bring these products up to the surface.
How to Optimize Internal Links for Better Page Depth
Here’s where things get actionable. Follow these steps to create an internal linking strategy that reduces page depth and boosts SEO:
1. Audit Your Current Structure
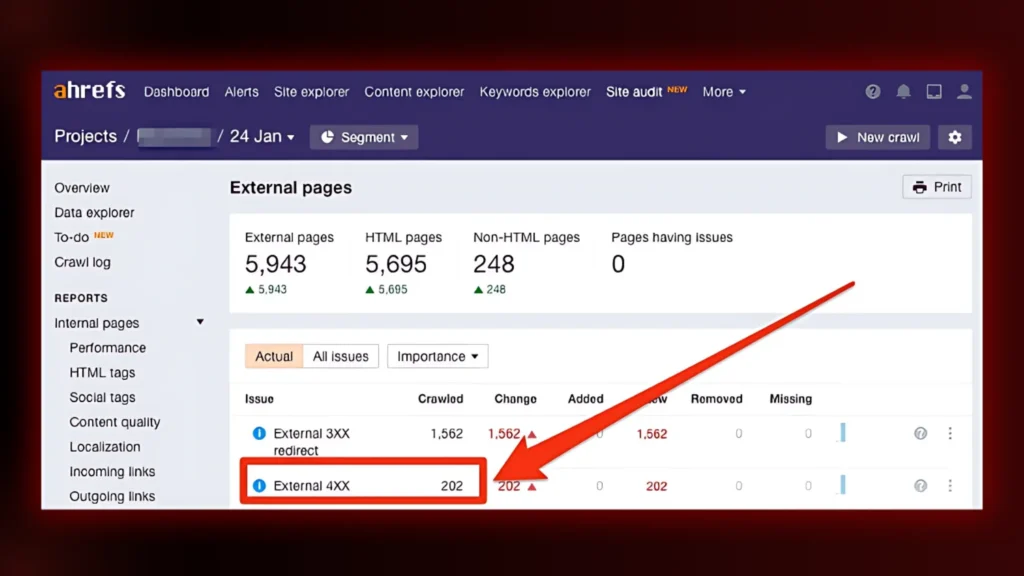
First of all, you draw up your website hierarchy. You can visualise how deep each page is using Screaming Frog or Ahrefs. Find pages which are more than three clicks from the main page.
2. Identify Key Pages

There are no two pages that are identical. Center your efforts on a page that brings traffic or conversions and make it easily accessible.
3. Use Descriptive Anchor Text

Anchor text should clearly describe what users can expect when they click the link. For example, instead of “click here,” use something like “learn more about internal linking strategies.”
4. Create Hub-and-Spoke Models
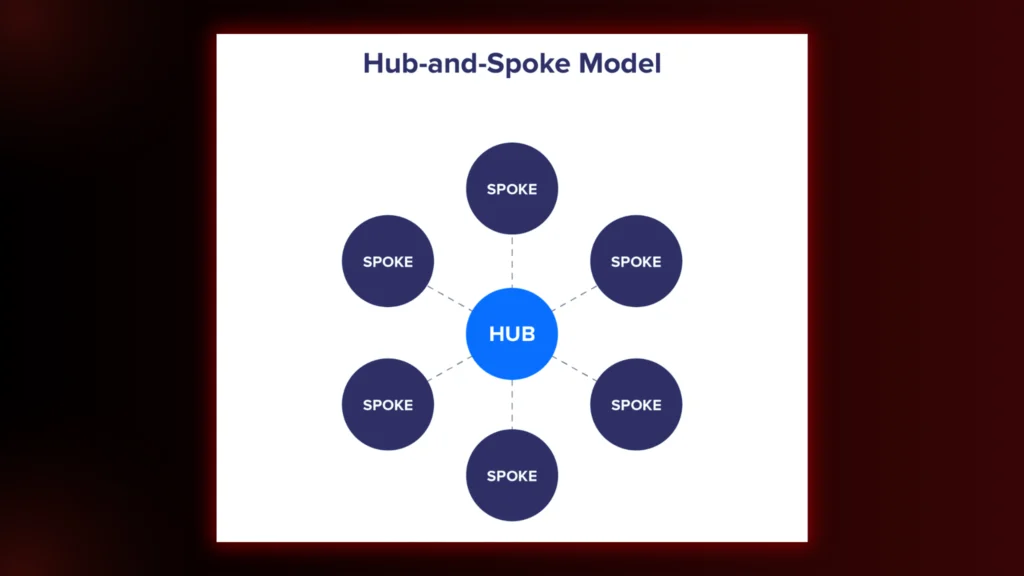
Think of this as creating content clusters. A central “hub” page links out to related “spoke” pages, and vice versa. This not only flattens your site structure but also improves topical relevance.
5. Add Contextual Links

Place internal links naturally within your content where they add value. For instance, if you’re discussing SEO basics in a blog post, link to a detailed guide on keyword research.
6. Leverage Navigation Menus

Your main menu and footer are prime real estate for internal links. Use them wisely to surface important pages.
Advanced Tips for Internal Linking
Once you’ve nailed the basics, take your strategy up a notch with these advanced techniques:
- Link From High-Traffic Pages: Pages that already rank well can pass on their authority through internal links.
- Support Long-Tail Keywords: Use internal links to target specific phrases that align with user intent.
- Update Older Content: Don’t forget about older blog posts! Add links to newer content where relevant.
- Avoid Overloading Links: Too many links dilute their value. Stick to 4-5 relevant internal links per page.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Even with the best intentions, it’s easy to go wrong with internal linking. Here are some pitfalls to steer clear of:
- Broken Links: These frustrate users and harm SEO.
- Over-Optimized Anchor Text: Using exact-match keywords excessively can trigger penalties.
- Ignoring Mobile Users: Ensure your links are easy to click on smaller screens.
- No Follow Tags on Internal Links: Always use dofollow tags so link equity flows freely.
Final Thoughts
Website page depth isn’t just an abstract concept—it directly impacts how users interact with your site and how search engines rank it. By combining a shallow site structure with a robust internal linking strategy, you can make sure every piece of content gets its moment in the spotlight.
So don’t let your best content stay hidden! Start optimizing today and watch as both traffic and rankings soar.
And remember: When in doubt, BrandClickX is here to help!
Contact us for further details!
FAQs
Q: How does website page depth affect SEO, and can internal linking help?
Website page depth impacts SEO by making it harder for search engines to crawl and index deeper pages. Internal linking can help by reducing page depth, making important pages more accessible and improving crawlability.
Q: What is the ideal website page depth for SEO, and how can internal linking strategies help achieve it?
The ideal website page depth is no more than three clicks from the homepage. Internal linking strategies can help achieve this by flattening your site structure and ensuring key pages are easily accessible.
Q: How does website page depth influence user experience, and can internal linking improve it?
A: Website page depth affects user experience by requiring more clicks to reach content. Internal linking can improve this by providing direct paths to relevant pages, reducing the number of clicks needed and enhancing overall navigation.



